
You will need the number of shares outstanding obtained from the income statement. You will only need to add the company’s market capitalization (easy to find on Google) and its price per share. If the book value is based largely on equipment, rather than something that doesn’t rapidly depreciate (oil, land, etc.), it’s vital that you look beyond the ratio and into the components. Companies with lots of machinery, like railroads, or lots of financial instruments, like banks, tend to have large book values.
Deceptive Depreciation and Book Value
BVPS is what shareholders receive if the firm is liquidated, all tangible assets are sold, and all liabilities are paid. The book value per share (BVPS) ratio compares the equity held by common stockholders to the total number of outstanding shares. To put it simply, this calculates a company’s per-share total assets less total liabilities. The market value per share is a company’s current stock price, and it reflects a value that market participants are willing to pay for its common share. The book value per share is calculated using historical costs, but the market value per share is a forward-looking metric that takes into account a company’s earning power in the future. With increases in a company’s estimated profitability, expected growth, and safety of its business, the market value per share grows higher.
Book value per share and tangible book value per share
It can offer a view of how the market values a particular company’s stock and whether that value is comparable to the BVPS. Investors can calculate it easily if they have the balance sheet of a company of interest. Investors can compare BVPS to a stock’s market price to get an idea of whether that stock is overvalued or undervalued.
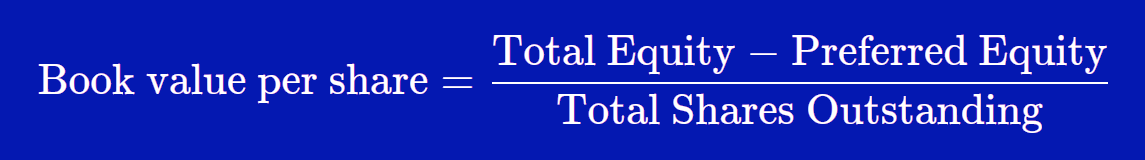
Book Value Per Share Formula
This means that, in the worst-case scenario of bankruptcy, the company’s assets will be sold off and the investor will still make a profit. Whereas some price models and fundamental analyses are complex, calculating book value per share is fairly straightforward. At its core, it’s subtracting a company’s preferred stock from shareholder equity and dividing that sum by the average amount of outstanding shares.
Book Value Per Share: Definition, Formula & Example
Earnings per share would be the net income that common shareholders would receive per share (company’s net profits divided by outstanding common shares). Let’s say that Company A has $12 million in stockholders’ equity, $2 million of preferred stock, and an average of 2,500,000 shares outstanding. You can use the book value per share formula to help calculate the book value per share of the company. Book Value per Share (BVPS) is the ratio of a company’s equity available to common shareholders to the number of outstanding company shares.
It depends on a number of factors, such as the company’s financial statements, competitive landscape, and management team. Even if a company has a high book value per share, there’s no guarantee that it will be a successful investment. This is why it’s so important to do a lot of research before making any investment decisions. If the company’s BVPS increases, investors may consider accountant reviews the stock more valuable, and the stock’s price may increase. On the other hand, a declining book value per share could indicate that the stock’s price may decline, and some investors might consider that a signal to sell the stock. By multiplying the diluted share count of 1.4bn by the corresponding share price for the year, we can calculate the market capitalization for each year.
But be sure to remember that the book value per share is not the only metric that you should consider when making an investment decision. There are a number of other factors that you need to take into account when considering an investment. For example, the company’s financial statements, competitive landscape, and management team.
If the BVPS is less than the price of the stock, then that tells an investor that the stock could be overvalued—it costs more than the assets it’s entitled to. On the other hand, when the BVPS is more than the stock price, that means an investor can essentially buy a share in a company’s assets for less than those assets are actually worth. Book value is the amount found by totaling a company’s tangible assets (such as stocks, bonds, inventory, manufacturing equipment, real estate, and so forth) and subtracting its liabilities. In theory, book value should include everything down to the pencils and staples used by employees, but for simplicity’s sake, companies generally only include large assets that are easily quantified. Book Value Per Share also theoretically reflects what shareholders would receive in a company liquidation after all its assets were sold and all of its liabilities paid.
Now, let’s say that XYZ Company has total equity of $500,000 and 2,000,000 shares outstanding. In this case, each share of stock would be worth $0.50 if the company got liquidated. The Book Value Per Share provides information about how the value of a company’s stock compares to the current Market Value Per Share (MVPS), or current stock price. For example, if the BVPS is greater than the MVPS, the company’s stock market may be undervaluing a company’s stock. Although infrequent, many value investors will see a book value of equity per share below the market share price as a “buy” signal. But an important point to understand is that these investors view this simply as a sign that the company is potentially undervalued, not that the fundamentals of the company are necessarily strong.
- Book value per common share (or, simply book value per share – BVPS) is a method to calculate the per-share book value of a company based on common shareholders’ equity in the company.
- There is also a book value used by accountants to value the assets owned by a company.
- BVPS is significant for investors because it offers a snapshot of a company’s net asset value per share.
- To get BVPS, you divide the figure for total common shareholders’ equity by the total number of outstanding common shares.
- You just have to click on the Price to tangible book ratio option to uncover these additional values.
Among these, the book value and the price-to-book ratio (P/B ratio) are staples for value investors. The book value per share of an undervalued stock is higher than its current market price, so book value per share can help investors appraise a stock price. If we assume the company has preferred equity of $3mm and a weighted average share count of 4mm, the BVPS is $3.00 (calculated as $15mm less $3mm, divided by 4mm shares). This formula shows the net asset value available to common shareholders, excluding any preferred equity. Book Value Per Share is calculated by dividing the total common equity by the number of outstanding shares.

